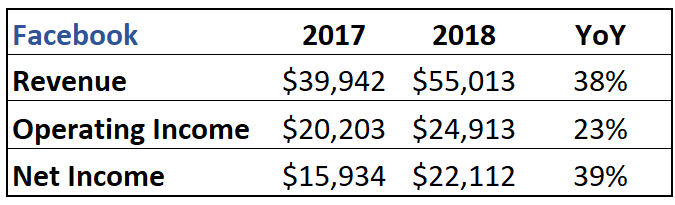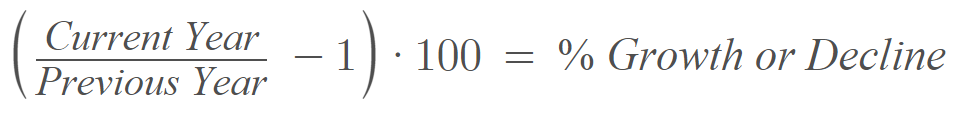Year-Over-Year (YoY) Analysis: Definition, Calculation and Examples
This article will help you find out everything you need to know about YOY, including what it’s all about and how to calculate it.
Know Salary of Accountant
How do you define YoY?
YoY is a term used to describe Year-over-Year and is an analysis of financials that is helpful when looking at the data of time series. Analysts can deduce changes in the quality or quantity of specific business elements using YoY analysis.
In finance, investors generally evaluate how financial instruments perform on a year-over year basis to determine whether or not the instrument is operating as it should. This method is helpful when looking at trends and growth patterns.
Economic analysts often employ this method when studying countries and their economic performance. For instance YoY is a popular method for analyzing the economic situation of a country. YoY method shows that Japanese GDP increased by 2 percent in 2016 when compared to 2015, whereas analysts were previously forecasting growth of 1.8 percent.
In financial analysis, year over year is a measure that is used to assess the performance of a company in a particular area in relation to the change from last year. It is regarded as an extremely efficient method of using an equation that is simple to draw financial trends when applied to the routine indicators of a company or other investments. YOY can be used to compare all metrics that are repeated every year, quarterly, or monthly in relation to your company’s reporting requirements.
One of the reasons YOY is a crucial metric is that it assists businesses in calculating fluctuations in seasonality in analyzing performance across all categories. It also gives an objective assessment of the overall performance.
For instance, year-over-year comparisons are an objective method of assessing a company’s overall sales performance since even during busy shopping seasons during the holidays the data won’t be affected to reflect the increase in the holiday season, as opposed to sequential analysis, which compares each month with the previous month.
It’s also a crucial aspect for retailers to research prior to beginning the holiday season since it helps them set targets for revenue that are reasonable in terms of the volume of traffic they’ll need to anticipate and also the growth in sales.
Analysis of YOY
What is Year-over-Year (YOY)?
Year-over-Year (YOY) is basically one of the most commonly employed financial comparator to evaluate two or more events that are measurable on an annual basis.
The YOY analysis allows to assess whether a company’s financial performance is growing or declining. For instance in financial reports, you might find that a specific business has reported increased revenues for the third quarter on a mainly YOY basis for the past three years.
The pros and cons Year over year
There are many reasons why executives may use YOY in order to get a better understanding of their financial health, and the benefits of this will be covered in this article, as will the disadvantages
The advantages of the YOY
Businesses employ year-over-year to produce the following outcomes:
Reduces the impact from seasonality in projections the comparison of two static points over time
Values that are volatile can be identified by comparing the overall results
Simple calculation that most people are able to do easily
Results are presented as percentages easy to comprehend to compare and gain immediate insights.
The disadvantages of the YOY
In the majority of instances, YOY isn’t really the only metric that businesses and investors depend on due to:
The results are enhanced by repeating the process across a variety of times
It’s not helpful to give information on specific months when performance could be enhanced
It is completely invalidated If one data point indicates negative growth
How do you calculate YOY?
To calculate YOY, you must follow these steps:
Select a metric which you can calculate the YOY value.
YOY is a useful indicator when compared to other measures. Most businesses focus on the year-over-year revenues, however they are able to apply any value that might be found on a regular financial report. This can include Earnings Before interest as well as Taxes (EBIT) and economic value-added net cash flow liquidity ratio, and many more. Be sure to select one or two values for YOY which will help you reach the most accurate conclusion regarding your company or investment.
Subtract two applicable data points
After you’ve chosen the data sets you’d prefer to work with, just subtract the numbers. The result of your formula would be the difference between the two numbers, which is then converted into a ratio during subsequent steps.
Divide the difference
Calculate the difference by the value of the previous year from the original equation. This should give you an answer in decimal.
Find a certain percentage
Then move your decimal point two spaces towards the right in order to calculate the percentage. You could round the percentage to the closest total number or work in decimals dependent on the degree of precision you require.
You can make your own calculation of year-over-year by filling in the following formula using two data points:
The YOY is (This year’s value minus the value of last year) or (Last year’s value)
Key TAKEAWAYS
year-over-year (YOY) can be described as a way of measuring two or more occasions to compare their results of one time period to the results of a similar period on an annual basis.
Comparisons of YOY are a well-known and efficient method of evaluating the financial performance of a firm.
Investors looking to evaluate the financial performance of a company can utilize YOY reports.
YoY and seasonality
The YoY method can also be beneficial in the analysis of growth in monthly revenue, especially in cases where the sources of revenue are more cyclical. This permits an apples-to-apples comparison of revenue, instead of comparison of revenue month-to-month, where there are likely to be huge seasonal fluctuations.
For instance, in the comparatively seasonally-based chocolate business, it may be more effective to examine the increase in revenue in December 2016, and the month of December 2017, (where the sales are at their highest because of sales during winter) instead of the comparison of March 2016 to February 2016, when holiday sales have begun to slow.
When comparing months year-over-year way it makes the comparison more important than two months in a row that are impacted by fluctuating seasons or other variables.
Common YoY financial metrics
Here’s a one of list of the most frequently used financial indicators to conduct an annual comparison:
How much has the sales increased, or declined over year
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) (COGS) – how has the business been able to control its gross margin
Selling General & Administrative expense (SG&A) How well have executives handled their corporate office expenses
Earnings before Interest Taxes, Depreciation and Amortization (EBITDA) is an indicator of operating profit and an indicator of cash flow
Net Income – a way of comparing your bottom line for the company over time
Earnings Per Share (EPS) is the bottom line per share basis
Understanding Year-Over-Year
Year-over-year (sometimes referred to as year-on year) comparisons are a well-known and efficient way to assess how a financial institution is performing business as well as the investment performance. Any event that is measurable and repeats every year can be evaluated to a YOY-based basis. Most YOY-related comparisons involve annual monthly, quarterly, and annual performance.
The common YoY economic indicators
Here’s a list the most frequently used measures to conduct a year-over-year comparison:
Inflation – What is the current trend in inflation?
What is the rate of participation in the workforce increase or decrease?
GDP – what gross domestic product can an economy producing
Rates of interest – are we in a falling or rising rates of interest?
Other alternatives to the YoY study
For a different approach in YoY analysis, analysts might want to take a look at other time-series information for example:
Month-over-Month
Quarter-over-Quarter
Year-to-date
Rates of compound growth
A good example YoY analysis
Here’s a thorough illustration for YoY analysis in real-time. This is an exercise in financial modeling where an analyst is comparing the amount of units sold during Q3 2018 with the amount of units that were sold during Q3 2017.
Let’s look at the YoY analysis step-by-step.
In Q3 2018, there were 506 units that sold during Q3 2018, and 327 units sold in Q3 2017. For comparison the two, we will multiply 506 by 327 and before subtracting one. The result is an increase of 55% in the number of units sold on a year-to-year basis from Q3-2018 to Q3-2017.
Benefits of Year-over-Year
YOY measures allow for the cross-comparison of different sets of data. For the company’s revenue in the first quarter by using YOY numbers, an analyst in finance or investor can review years of data on revenue from the first quarter and quickly find out if the revenue of a business is growing or declining.
In the initial quarter in 2021, the Coca-Cola corporation posted an increase of 5% in its net profits in comparison to the same quarter last year. If you compare the same times in different years, it’s possible to draw precise comparisons, despite the nature of seasonal consumer behavior.1 The YOY comparison can be useful for investing portfolios. Investors love to study the YOY’s performance to determine how it changes over time.
The Reasons Behind Year-over-Year
Comparisons of YOY are popular when looking at the performance of a business because they reduce the effects of seasonality, which affects the majority of companies. Profits, sales and other financial indicators vary throughout the year since many lines of business experience high demand and low-demand season.
Retailers, for instance, have an extremely high demand period in the season of Christmas shopping that falls during this fourth quarter. To measure the business’s performance, it makes sense to measure revenues and profits year-over year.
It is important to evaluate the fourth-quarter results in one year with the performance of the fourth quarter in previous years. When an investor examines the performance of a retailer in the fourth quarter and compare them to the 3rd quarter results, it could seem like a company is experiencing an unprecedented expansion, even though it’s seasonality is the reason for the variance in performance.
Similar to a comparison between the 4th quarter with the next quarter the first quarter could show an extreme drop, but this could be the result of seasonality.
YOY differs from “sequential,” which measures the ratio of one quarter or month in relation to the preceding one and permits investors to view the growth in linear fashion. For example, the number of cell phones that a firm sold in the fourth quarter, compared to 3rd quarter or even the number of seats that airlines booked in January, compared to December.
Real-World Example
In an annual NASDAQ announcement, Kellogg Company released mixed results for the fourth quarter of 2018, which revealed that year-over year earnings continue to fall, despite the fact that sales have risen following corporate acquisitions. Kellogg estimates that its adjusted earnings will fall by another 5-7% to 7% in 2019 since they continue to make investments in alternative packaging and channel formats.2
The company also has revealed plans to organize it’s North America and Asia-Pacific segments and remove several departments from its North America segment and reorganizing its Asia-Pacific segment into Kellogg Asia, Middle East, and Africa. Although earnings have decreased year over year however Kellogg’s strong presence and the ability to react to consumer preferences mean that Kellogg’s outlook overall is positive.
What are the purposes of Year-over-Year?
YOY is utilized to draw comparisons between a time period and another which is one year older. This permits an annualized comparison, such as of third-quarter earnings this year and. third-quarter profits from a one year prior. It is typically utilized to evaluate a business’s growth in revenue or profits and is also used to define annual variations in the economy’s currency supply or GDP, gross domestic product (GDP) as well as other economic measures.
How is Year-Over-Year Calculated?
The calculations for YOY are easy and are usually expressed in terms of percentage. It involves taking the value for the current year and then dividing it by the previous year’s value, then subtracting the following: (this year)/(last year) 1.
What is the difference between the two terms YOY and YTD?
YOY examines a 12-month change. Year-to date, or YTD is a measure of change relative to the start of the year (usually January 1st).
What If I’m Interested in Comparatives for less than One Year?
You can compute month-over month (MoM) and quarter-over quarter (QoQ) similarly to similar fashion to YOY, as well as for any other timeframe that you want.
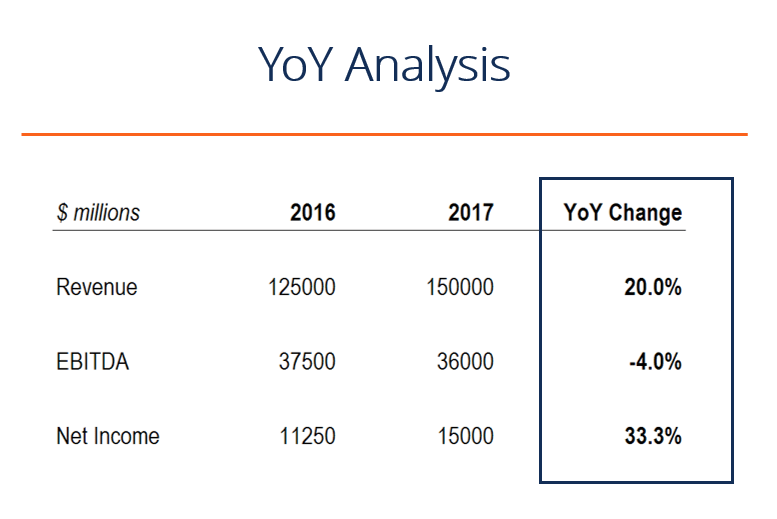
The numbers at the bottom of the table indicate changes in the YOY. In this instance it’s all positive which is optimal. We’ve also adjusted the percents to round numbers.
If math isn’t your best capability, or you love being precise and consistent in your calculations There are numerous internet-based tools as well as resources at the workplace that will aid you in calculating the year-over-year figures for analysis of financials, and other crucial indicators that your company could employ to stay in front of your competitors.
Examples of YOY
Here are a few examples of companies that make use of the YOY insight:
Example 1. Nutritional Food Co.
Nutritional Food Co. found that the company had mixed results in its fourth quarter. YOY Analyzing revenue showed that the company’s profits decreased despite the acquisitions, which increased sales overall. The decrease was anticipated, and the company is expecting annual earnings to decline as they buy more businesses to expand the market shares of their companies.
If this year-over-year figure is considered on its own, this paints an image of Nutritional Food Co. that could appear to be to be bleak. But the company that is an international distributor of nutritional products plans to streamline its activities across North America and Asia, which is expected to boost sales once the initial investment is completed. When you look at the whole picture of Nutritional Foods Co. It is seeing a decrease in their YOY in the present time, but other statistics show that they’re on track for growth.
Example 2: Government agencies
Revenue isn’t the only factor that businesses employ to measure the growth and performance of their business.
The government agencies typically present financial data in month-to-month or quarter-to-quarter view, however to see the full picture, year-over year financial data is required. The government utilizes these three indicators to calculate year-over-year data to assess the state of the economy in which it is doing
Manufacturing jobs: Year-over year declines in manufacturing jobs showed the beginnings of a recession.
GDP: Gross domestic product, examined year-over-year is the amount the nation could produce in goods if the growth was at its most stable rate. It will tell you if the economy is growing or declining.
Durable products: The huge number of huge, durable investments that businesses in America invest in each year is an indicator of their overall performance. If they look at the year-over-year performance of economists, they are able to determine whether the rate of success is growing or declining.

My Name is Nadeem Shaikh the founder of nadeemacademy.com. I am a Qualified Chartered Accountant, B. com and M.Com. having professional and specialize experience in field of Account, Finance, and Taxation. Total experience of 20 years in providing businesses solution in Taxation, Accounting, and Finance with all statutory compliance with timely business performance Financials reports. You can contact me on nadeemacademy2@gmail.com or contact@nadeemacademy.com.