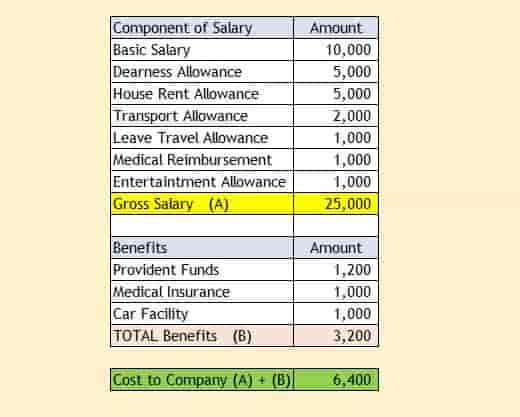
Introduction of Gross Salary
Our careers many times usually play a very critical role in making us a responsible type of individuals. For some people, making a career or getting a job is to pass the time, but it can be a good source of income for others, and for a few people, their work can be their life.
Therefore, we will see that a large number of people are joining the active known workforce daily. Also, it is not to mention that the enthusiasm which is associated with our first starting job is always been indefinable. But, when it is compared to your first salary, it is quite surprising.
Your first salary will leaves you in a baffled because of the salary which is mentioned by the company was in name as X.
INR, but you may have received less amount than has been said.
‘Where’s the rest?’ is the most known common type of question that may arises in your mind as a fresher.
However, it is not many know that there is a difference between net take-home salaries, Cost to company and a gross salaries. Now lets us discuss one of these important elements, known as Gross Salary, in deep detail.
What is a Gross Salary?
Many employees are normally paid for their services that are also been offered as a gross salary as their Cost to Company. Cost to the company is a amount that of a money that the company has to be incur on an employee for been a particular or a specific year. But, the point is here that it is to remember as here is that cost to the company can be never be equal to amount of a money that any employee can take home.
In easy terms, Gross Salary is basically a monthly or a yearly amount of salary before any type of a deductions that are made from it.
OR
A gross salary we need to not include gratuity and a employer provident fund can be subtracted from the calculation of cost to the company. The components of Gross salary that normally consists of following:
Basic Salary
House rent allowance
Special Allowance
E.A. Educational Allowance
C.A. Conveyance Allowance
M.A. Medical allowance
LTA Leave travel allowance, etc.
Below are well known components that basically form a part of Gross Salary-
Other components will include remuneration, salary arrears, or fee, overtime payment, and performance type of related cash awards.
Benefits such as rents for accommodation, electricity bills, fuel charges, and water.
Allowances like known as medical allowance, travel allowance, leave travel allowance, etc.
Explanation of a gross salary components:
Basic Salary: Basic salary is also considered as the actual amount that is paid to the employee before any type of deductions are made. Or even extra any components which are added to salary. Besides, the basic salary can always be lower than the gross salary or even the take-home salary.
Perquisites: These are a considerable amount of benefits which an employee receives due to their position in an organization and are payable and also the salary which is received by them. Besides this, benefits can be taxable as well, as they can be non-taxable, but it depends upon their nature.
Salary Arrears: Most of us are well with familiar with known term as arrears. For a definition, arrears refer to an amount paid due to an increment in your salary.
House rent allowance: A House Rent
Allowance can also be one of the major salary components paid by the employer to their employees for accommodation expenses. Also, the HRA applies to both salaried and self-employed individuals.
More Salary will reduce Company Profit Margin.
Components that are not a part of gross salary-
Few components do not form a part of the gross salary paid by the employer to an employee of his organization, such as:
The employer provides refreshments and snacks to his employees during office hours.
Reimbursement for travel and even expenses for food for official/business purposes.
Calculation of gross salary-
The gross income can often be a figure required by the lenders while deciding whether or not to advance credit for an individual. This same applies to the landlords while determining whether a potential tenant can pay their rent on time. It is also the starting point while calculating taxes due to the government.
Gross Income for an Individual:
The gross income is the amount of money earned before any deductions or taxes are taken out. An individual employed full-time has their annual salary or wages before tax as their gross income. However, a full-time
Employees might also be having other sources of income that must be taken into consideration while calculating their income.
E.g., any dividends on stocks that an individual can hold should be included in the gross income. Other incomes that should be considered, including the income from rental property and interest income from investments and savings.
E.g., Assume that Johny earns an annual income of 100,000 USD from his particular consultancy work. Johny also earns 70,000 USD in rental income from his various real estate properties, 10,000 USD in dividends from the shares which he owns at Company ABC, and 5,000 USD in interest income from his savings account.
Calculation of Johny’s income can be done as follows:
Gross Income = 100K + 70K + 10K + 5K =
185K USD.
Gross Income for a Business:
Gross profit is a term or an item in the income statement of a business, and it is the company’s gross margin for the year before deducting any indirect expenses, interest, and taxes. It represents the revenue that a company earned from selling its goods or services after subtracting the direct costs of producing the goods being sold.
Direct costs can include the cost of labor, equipment used in the production process, supply costs, amount of raw materials, and shipping cost. Taxes are not deducted as they cannot be directly related to the production and sale of the product.
The formula for the calculation of the gross income, or gross profit, of a business, is as follows-
Gross income is equaled to the Gross Revenue subtracted with the Cost of Goods Sold to get profit Margin.
E.g.,
Let’s assume that the gross revenue of ABC, which is considered as a paint manufacturing company having totaled 1,300,000 USD, and the expenses were as follows:
Cost of raw materials: 150,000 USD.
Supply costs: 60,000 USD
Cost of equipment: 340,000 USD
Labor costs: 150,000 USD
Packaging and shipping: 100,000 USD
Calculation of the Gross profit:
Gross Income = (1,300K) – (150K + 60K + 340K + 150K + 100K)
= (1,300K) – (800K)
= 500K USD
Gross salary Vs. Net income-
Gross income is considered the total of all incomes from providing all services to the clients before various deductions, taxes, and specified other expenses.
Net income is the profit that is attributable to a business or individual after subtracting all their expenses. A company can calculate net income by subtracting all the professional and legal fees like business expenses, taxes due, advertising costs, interest expenses, and any eligible deductions.
If the net income is considered as a positive value, then it is a profit, but it shows that it incurred a loss if it is negative.
Significantly if the difference between gross profit and net income is higher, then it can show that it can incur many expenses. In such a situation, its expenses should review the business to eliminate unnecessary expenses and reduce necessary expenses.
For an individual, net income is earned after deducting state and federal taxes, social security taxes, health insurance, etc.
What is the cost to the company?
The Cost to Company is the amount decided by the company at the time of recruitment of an employee. It also involves other elements such as the
House Rent Allowance, Gratuity, Provident Fund, and Medical
Insurance, among other allowances, is added to the basic salary. In other words,
Cost to the Company is a term that is considered in the total salary package of an employee. It can also indicate the cumulative amount of expenses an employer spends on an employee during one year.
A CTC consists of the total of Direct Benefits (sum paid to an employee every year), Indirect Benefits (sum the employer pays on behalf of the employee), and Saving Contributions (saving schemes they are entitled to). Therefore, CTC = Direct Benefits + Indirect Benefits + Savings
Contributions.
More about gross salary-
The amount received post subtracting gratuity and the employee provident fund (EPF) from Cost to Company (CTC) is Gross Salary. In other words, the Gross Salary is the amount paid before the deduction of taxes or deductions and is inclusive of bonuses, overtime pay, holiday pay, etc.
In India, the Employees Provident Fund is an employee-benefit scheme recommended by the Ministry of Labour, which helps provide employees with an income after past years. The Employee Provident Fund Organization has the authority to mandate policies on EPF, pension, and insurance schemes.
However, the employer must contribute at least 12% of the employee’s salary towards their Employees Provident Fund.
An Employee also have an option to withdraw the full amount accumulated in their PF account at the time of retirement, which is when the employee attains 55 years. Although, they can also withdraw the PF amount in case of the following situations:
Migration of the employee to a foreign country.
In this case, the employee who is retired due to permanent disability.
Termination of services.
Calculation of PF in gross salary-
The calculation of Gross pay for Provident Fund calculation is different from that used in the payroll context. Let us consider Provident Fund Gross to denote the salary to be considered for calculating the Provident Fund.
Provident Fund Gross includes Basic, DA, Conveyance, Other Allowance,
etc. (heads of pay included for provident fund calculation). In this calculation, House Rent
Allowance, Bonus, etc., are excluded as per the provisions of the PF Act.
Deduction from gross salary-
For calculating the Income Tax, gross salary, which is deducted from the eligible deductions, has been considered. For instance: you might also have to subtract HRA exemption, any home loan EMI, investments under sections 80C and 80D, and similar things to calculate taxable income.
Please note: The taxation process can be different for Self-employed and salaried individuals.
Gross salary under section 17(1)-
As per income tax section 17(1), salary will includes the following
Amounts received by an employee from his employer during the previous year.
Wages.
Any advance of salary.
Various fees, commissions, gratuities, or profits can be in addition to any salary or wages.
The contribution is made by the Central Government or any another employer in the previous year to the account of an employee under a pension scheme referred to in Section 8OCCD.
He does not receive any payment from an employee regarding any leave period; (Leave encasement or salary instead of leave).
The aggregate of all the total’s that have been comprised in the transferred balance as according to the reference of the sub-rule (2) of Rule 1 of Part A of the
4th Schedule, of an employee participating in a recognized provident fund, to the extent to which it is chargeable to tax, under sub-rule (4) there, i.e., the taxable portion of transferred balance from an unrecognized provident fund to the recognized provident fund.
The annual growth or increase by the gradual accumulation to the balance at the credit of an an employee participating in a recognized provident fund, to the extent to which it is chargeable to tax under Rule 6 of part A of the Fourth Schedule.
Example of gross salary and net salary-
Sumita is working as a Marketing Manager with XYZ Group Ltd.
His gross salary per month is 70,000 INR, while his net-take home is just 56,000 INR.
Salary Components:
Basic Salary = 25,000 INR
HRA = 20,000 INR
LTA = 10,000 INR
Travel Allowance = 15,000 INR
Total = 70,000 INR
Deductions:
Provident Fund – 3000 INR
Income Tax – 1500 INR
Profession Tax – 500 INR
Loan Deduction – 9000 INR
Total Deductions – 14,000 INR
Therefore, Net Salary = Gross Salary – Deductions =
70,000 INR – 14,000 INR = 56,000 INR.

My Name is Nadeem Shaikh the founder of nadeemacademy.com. I am a Qualified Chartered Accountant, B. com and M.Com. having professional and specialize experience in field of Account, Finance, and Taxation. Total experience of 20 years in providing businesses solution in Taxation, Accounting, and Finance with all statutory compliance with timely business performance Financials reports. You can contact me on nadeemacademy2@gmail.com or contact@nadeemacademy.com.