What are financial ratios?
Financial ratios are very useful tools that help business managers and investors to analyse and compare the financial relationships between the accounts on the firm’s financial statements. They are tools that make financial analysis possible across a company’s history, an industry, or even a business sector.
Financial ratio analysis is used for gathering the data from calculating the ratios to make decisions about improving a firm’s profitability, solvency, and liquidity.
Introduction of Financial ratios analysis
Financial ratio analysis is one quantitative tool that business managers use to gather valuable insights into a business firm’s profitability, solvency, efficiency, liquidity, coverage, and market value.
Ratio analysis provides this information to business managers by analyzing the data contained in the firm’s balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows.
The information gathered from Financial ratios analysis is invaluable to managers who have to make financial decisions for the business and to external parties, like investors, to evaluate the financial health of the business.
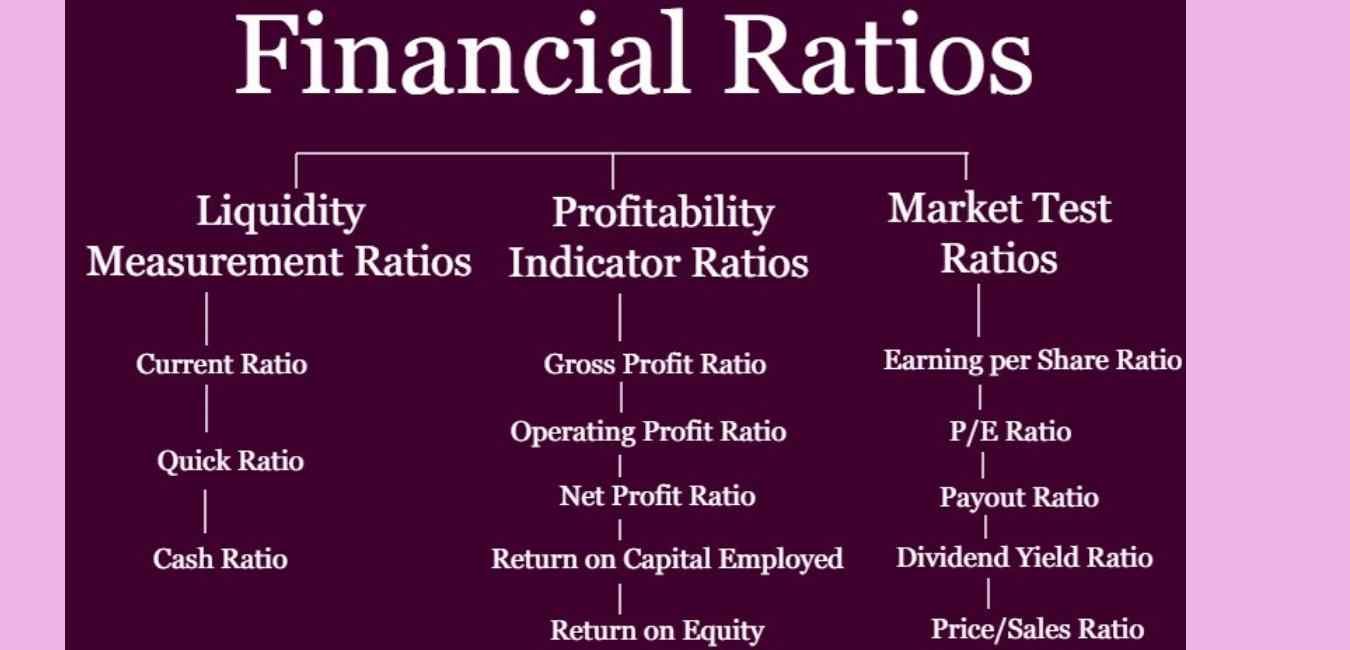
Types of financial ratios
Liquidity ratio:
Liquidity ratios analysis is the ability of a company to pay off both its current liabilities as they become due and its long-term liabilities as they can become current.
In other words, these ratios can show the cash levels of a company and even the ability to turn other assets into cash for paying off the liabilities and other current obligations.
Liquidity is not only used as a measure of how much cash a business is having, but it is also a measure of how easy it will be for the company to raise enough cash or converting assets into cash.
Assets like trading securities, accounts receivable, and even a inventory are relatively easy for many of companies to convert it into cash in short term. Thus, all of these assets go into the liquidity calculation of a company. This improve your quick ratio.
Solvency ratio
Solvency ratios are also called leverage ratios. It measures a company’s ability to sustain operations indefinitely compared to the debt levels with equity, assets, and various earnings. In other words, solvency ratios can be identified, which will concern issues and a firm’s ability to pay its bills in the long term.
Many people usually confuse solvency ratios with liquidity ratios. Although they both can measure the abilities of a company to pay off its obligations, solvency ratios can focus more on the long-term sustainability of a company instead of paying the current liabilities.
Solvency ratios indicate a company’s ability to make payments and pay off its long-term obligations to creditors, bondholders, and banks. Better solvency ratios will indicate a more in creditworthy and a financially sound company in long term.
Efficiency ratio
Efficiency ratios are also called activity ratios; it helps measure how well companies utilize their assets to generate income.
Efficiency ratios often look when it takes companies to collect cash from a customer or the time it takes for the companies to convert inventory into cash; in other words, it makes sales.
The management can use these ratios to help to improve the company and outside investors and creditors to look at the profitability of the company.
Efficiency ratios will go hand in hand with a profitability ratios. Most often, when the companies are efficient with their resources, they become profitable.
For example, Wal-Mart is extremely good at selling low-margin products at higher volumes.
In other words, they are very much efficient in turning their assets. Even though they do not make much profit per sale, they make a ton of sales. Each short sale adds up.
Profitability ratio
It can compare profitability ratios to the income statement accounts, and it is categorized to show a company’s ability to generate profits from its operations.
Profitability ratios can focus on a company’s return on investment in inventory and other assets. These ratios usually show that how well companies are achieving profits from their operations.
Investors and creditors can use profitability ratios for judging a company’s return on investment based on the relative level of resources and other assets.
In other words, the profitability ratios can be used for judging whether companies are capable of making enough operational profit from their assets.
In this sense, profitability ratios can be related to efficiency ratios because they show how well companies use their assets for generating profits in Financial ratios. Profitability is also important for the concept of solvency and going concerned.
Market prospect ratio
Market Prospect ratios can be compare publicly-traded companies. Like stock prices with a several other financial measures like dividend rates and earnings. Investors use the market prospect ratios for analyzing stock price trends and help for figuring out a stock’s current and future market values.
In other words, market prospect ratios show the investors what they should expect to receive from their investment. They might also receive future dividends, earnings, or just even an appreciated stock value.
These ratios are very helpful for the investors to predict that how much will need stock prices in the future based on current earnings and measurements of the dividends.
For instance, a downward trend in earnings per share and dividend yield points to profitability problems and could raise ongoing concerns. All of these issues can point towards a lower stock evaluation.
Financial leverage ratio
Financial leverage ratios, sometimes also called equity or debt ratios, measure the value of equity in a company by analyzing its overall debts. These ratios are either used for comparing debt or equity to assets and even shares outstanding for measuring the true value of the equity in a business.
In other words, the financial leverage ratios can be used for measuring the overall debt load of a company and compare it with the assets or equity.
It shows that how much of the company assets belong to the shareholders rather than with the creditors. When shareholders own a majority of the assets, then the company is said to be having less leveraged.
When the creditors own the majority of the assets, the company is considered to have high leverage. These measurements are important for investors to understand how risky a company’s capital structure is and its worth for investment.
Coverage ratio
Coverage ratios are the comparisons that are designed for measuring the company’s ability to pay its liabilities. On the surface, mainly a coverage ratios will might sound a most of like a liquidity and a solvency ratios, but there is a distinct type of difference. Coverage ratios which analyze any company’s ability to mainly service its debt and any other obligations.
In other words, these type of ratios measure how well a companies can afford mainly to make the interest payments associated with the debt. Some ratios are also include in obligations that are not mainly not typical liabilities, like regular which pays dividend payments to its stockholders.
Receivables turnover ratio
Accounts receivable turnover is counted as an efficiency ratio or an activity ratio that helps measure how many times a business can turn its accounts receivable into cash during a year.
In other words, the accounts receivable turnover ratio can measure that how many times a business can collect its average accounts receivable during the year.
In turn, it is referred that each time a company collects its average receivables and If a company is having 20,000 USD of average receivables during the year and collects 40,000 USD of receivables during the year, then the company would have to turn its accounts receivable twice because if it collected twice the amount of average receivables, then this ratio can show that how efficiently a company is collecting its credit sales from customers.
Some companies can even collect their receivables from customers in 90 days, while others take up to 6 months to collect from customers.
In some ways, a receivables turnover ratio will be viewed as one of liquidity ratio as well. Companies are more then liquid then the faster they will convert their accounts receivables into a cash.
Asset turnover ratio
The asset turnover ratio is also an efficiency ratio that helps measure its ability to generate sales from its assets compared to the net sales with average total assets. In other words, this ratio can also show that how efficiently a company is using its assets for generating sales.
The total asset turnover ratio can also calculate net sales as a percentage of assets to show how many sales have been generated from each dollar of company assets. For instance, if there is a ratio of .5, then that means that each dollar of assets is generating 50 cents of sales.
Cash conversion cycle
Calculation of any cash conversion cycle is mainly a cash flow. This attempted to mainly measure the time it will takes to convert its existing investment in inventory. Also in other resource which will inputs into cash. In other words, the cash conversion cycle calculation measures how long cash is tied up in inventory before the inventory is sold and cash is collected from customers.
The cash cycle has three distinct parts. The first part of the cycle mainly represents the current level of inventory and on how long it will basically take the company to sell this type of inventory. This stage is calculated by using the day’s inventory outstanding calculation.
The second stage of the cash cycle represents the current sales and the amount of time it takes to collect the cash. It is calculated by using the day’s outstanding sales calculation.
The third stage represents the current outstanding payables. In other words, this mainly represents on how much a company will owes its current vendors for an inventory and that goods purchases. When the company will be paying off its vendors. It is calculated by using the day’s payables outstanding calculation.
Compound annual growth rate
Compound Annual Growth Rate and financial investment calculation helps in measuring the percentage an investment increases or decreases year over year.
You can even think of this as the annual average rate of return for an investment over some time.
Since most investments’ done annually returns vary from year to year, the CAGR calculation is the average of good years’ and bad years’ returns into one return percentage used by all the investors and management to make future financial decisions.
It is also important to be remembered that the compound’s annual growth rate percentage is not the actual annual rate of return. It is an average of all the annual returns the investment has produced. It evens all the years’ rates out to make it easier than the returns to other investment opportunities.
For example, if a company is funding a capital project that loses money for five straight years and makes a huge profit on the sixth year. This CAGR would even out the first five years’ worth of negative returns with the sixth year’s positive return.
Contribution margin
Sometimes used as a ratio, the contribution margin is the difference between its total sales revenue and its variable costs. In other words, the contribution margin is equalled to the amount that sales exceed variable costs. It is the sales amount that can be used to or contribute to paying off fixed costs.
The concept of this equation completely relies on the difference between fixed costs and variable costs. Fixed costs are the production costs that remain the same as there is an increase in the production efforts. Variable costs, on the other hand, are increased with the company’s production levels.
The contribution margin helps measure how efficiently a company produces its products and maintains low levels of variable costs. It is mainly considered a managerial type of ratio because companies may rarely report margins to a public. Instead this management who regularly uses this calculation which will help improve internal procedures in the part of production process.
Current ratio
The liquidity of a current ratio is an efficiency ratio that helps measure a firm’s ability to paying off its short-term liabilities with its current assets. The current ratio is one of an important measure of a liquidity because its short-term liabilities are mainly that due within the next year.
It means that a company has a limited amount of time to raise funds to pay for these liabilities. It can easily convert current assets like cash, cash equivalents, and marketable securities into cash in the short term.
It means that companies with larger amounts of current assets will more easily pay off current liabilities when they become due without having to sell off long-term, revenue-generating assets.
Day’s sales in inventory
The day’s sales in inventory calculation, also called days inventory outstanding or simply days in inventory measures the number of days it will take a company to sell all of its inventory. In other words, the day’s sales in inventory ratio show how many days a company’s current stock of inventory will last.
It is important for the creditors and investors for three main reasons. It usually measures the value, liquidity, and cash flows.
Both investors and creditors want to know that how valuable a company’s inventory is. Older, it is more obsolete inventory always worth less than current, fresh inventory. The day’s sales in inventory show’s that how fast the company is moving its inventory. In other words, it also shows that how fresh the inventory is.
This calculation also shows the liquidity of the inventory. Shorter days inventory outstanding means that the company can convert its inventories into cash sooner. In other words, basically inventory is extremely a liquid.
Along the same line, more the liquid inventory which will means the more will be company’s cash flows get better day by day.
Debt ratio
The debt ratio is a solvency ratio that normally measures its total liabilities as a percentage of its total assets. In a sense, the debt ratio indicates its ability to pay off its liabilities with its assets. In other words, this also shows how many assets the company must sell to pay off all of its liabilities.
This ratio can also help in measuring the financial leverage of a company. Companies having higher levels of liabilities compared with assets are considered highly leveraged and riskier for lenders.
It helps investors and creditors analyse the overall debt burden on the company and the firm’s ability to pay off the debt in future, uncertain economic times.
Debt service coverage ratio
A financial ratio which is known as the debt service coverage ratio, helps in measuring the company’s abilities to serve its current debts by comparing its net operating income with its total debt service obligations. In other words, we can compare this ratio with the company’s available cash with its current interest, principle, and even sinking fund obligations.
The debt service coverage ratio is considered important for both the creditors and investors, but creditors most often analyse it. Since this ratio helps measure the firm’s ability to make its current debt obligations, current and future creditors are particularly interested in it.
Creditors want to know the cash position and cash flow of a company, but they also want to know how much debt it currently owes and the available cash to pay the current and future debt.
Unlike the debt ratio, the debt service coverage ratio considers all expenses related to debt, including interest expense and other obligations like pension and sinking fund obligation. In this way, the DSCR is just like telling of a company’s ability or commitment to pay his debt than the debt ratio.
Debt to equity ratio
The financial liquidity ratio, also known as the debt to equity ratio, compares a company’s total debt to total equity.
The debt to equity ratio also shows the percentage of company financing collected from the creditors and the investors. A higher debt to equity ratio can indicate that more creditor financing (bank loans) is used than investor financing (shareholders).
Dividend payout
The dividend pay-out ratio is also used to mainly measure a percentage of a net income distributed. Among the shareholders in the form of known as dividends during the financial year. In other words, this ratio indicates the portion of profits that the company has decided to keep to fund operations and the portion of the profit shared with the shareholders.
Investors are normally interested in the dividend pay-out ratio because they want to know if companies are paying a reasonable portion of net income to investors. For instance, most start-up companies and tech companies rarely give dividends at all. Apple, a company established in the 1970s, just gave its first dividend to the shareholders in 2012.
Conversely, some companies mainly wanted to spur investors’ as a interest, So much that they will be paying out unreasonably with high dividend percentages. Inventors can’t sustain these dividend rates very long because they will eventually need money for their operations.
Explanation of the Pros of the use of Financial ratios
Helpful in setting goals for high performance
By analysing the financial ratio, financial and business managers can be determined which is also an acceptable financial performance for the business firm. The firm can see a real performance by viewing its performance across time and aspire to better performance by looking at the industry leader’s financial data.
Useful for small firms with a narrow focus or divisions of large firms
Large and multidivisional firms do not find financial ratio analysis useful for the firm as a whole. Since ratios are only useful compared to industry or firm financial data, smaller firms with one line of business or the divisions of larger firms find ratio analysis useful.
Useful to analyse a firm performance across periods
Time-series or trend financial ratio analysis lets firms evaluate financial performance across periods such as a quarter or a fiscal year.
Useful to mainly to compare firms on a industry basis and
cross-sectional or Comparing a firm’s financial performance to a group of similar firms within an industry allows the financial manager to see where the firm stands competitively.
Explanation of the Cons of the use of financial ratios
Not useful for large, multidivisional firms
Since ratio analysis is useful only on a comparative basis, divisions of large firms can also be useful for this financial analysis technique. Still, it is not useful for a multidivisional company as a whole.
Problems if there is inflation
If the business firm operates in an inflationary environment, then the financial data will be distorted from one time to another, and the ratio analysis will not be useful.
Window dressing
Firms can cheat, and even window dress their financial statements. Window dressing is usually the act of making financial statements that looks stronger but manipulating data.
Seasonal and cyclical firms
If business firms have seasonal or cyclical sales, financial ratio analysis using time-series data will yield distorted results since sales vary widely between periods.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Financial ratios?
A financial ratio or accounting ratio is relatively a magnitude of two selected numerical values taken from an enterprise’s financial statements. Often used in accounting, many standard ratios are used for evaluating a corporation’s overall financial condition or other organization.
What is good financial leverage ratio?
0.5 Or fewer numbers can be considered ideal. Then, in other words, no more than half of the company’s assets can be financed by debt.
In other words, a debt ratio of 0.5 can be necessarily mean that the debt to equity ratio of 1. A lower number normally indicates a company that is less dependent on borrowing for its operations in both cases.

My Name is Nadeem Shaikh the founder of nadeemacademy.com. I am a Qualified Chartered Accountant, B. com and M.Com. having professional and specialize experience in field of Account, Finance, and Taxation. Total experience of 20 years in providing businesses solution in Taxation, Accounting, and Finance with all statutory compliance with timely business performance Financials reports. You can contact me on nadeemacademy2@gmail.com or contact@nadeemacademy.com.